Solution Overview
3 Solution Overview
Arcology is a high-performance and general-purpose enterprise blockchain system. To comprehensively address all the issues mentioned above, there is a need for systematic rethinking and re-architecting of current system design concepts. We carry this vision throughout the entire R&D process.
Our innovations are centered around the following key points.
3.1.1 Cluster Computing
An Arcology node is a cluster of commodity computers with different services deployed on multiple machines and connected by a high-speed network. Multiple machines can work collaboratively to share the workload. There is no upper limit on the number of computers that can be added to the cluster.
Arcology’s super-computer network has achieved unmatched performance.
Additionally, Arcology features supercomputer-level parallelism. Transactions are distributed to multiple cores and multiple processors for parallel processing, thereby making full use of computational power.
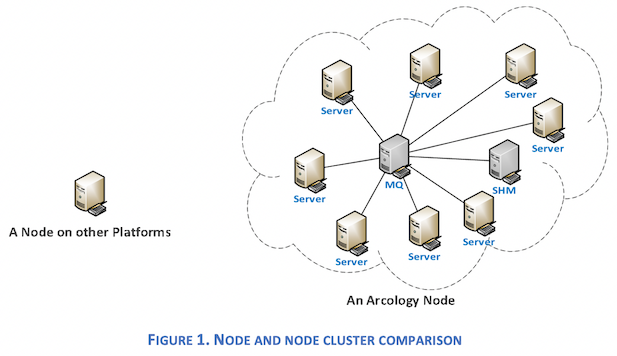
Because Arcology adjusts computational resources on the fly, improving throughput is simple as adding more machines to the cluster.
3.1.2 Deterministic Concurrency
Cluster computing is more than just physically connecting a cluster of computers. To fully harness the computational power a cluster of hardware, Arcology’s concurrency design is responsible for the following tasks:
- Divide and encapsulate transaction processing module
- Manage computational resources
- Coordinate transaction processing over the network
- Guarantee deterministic concurrency
- Collect processing results
- Detect conflicts caused by misuse
- Schedule tasks
- Provide smart contract language-level support to shared resource access
Arcology’s concurrency mechanism is fully deterministic, which guarantees that any given transaction will yield the same result regardless of hardware configurations or software environment.
3.1.3 Tiered Storage
Arcology has a carefully designed tiered storage framework that helps achieve maximum performance while keeping costs low. Specifically, the data store is abstracted into a data storage service running in node clusters.
Users can choose the storage configuration that best suits their needs. In Arcology, a delicate balance between cost reduction and data safety is maintained through storage sharing.
3.1.4 Consensus
Arcology uses a consensus algorithm called “Multifactoring” that features a built-in mechanism to guarantee incentivizes for contributing nodes. This is essentially for the long-term health and robustness of the network.
3.1.5 Intelligent Network Communication
Arcology automatically adjusts its network communication parameters to adapt to ever-changing network conditions ensuring the best throughout with the lowest possible latency. To maximize bandwidth, Arcology allows multiple connections to be established. To achieve this, the network communication module uses machine learning algorithms to automatically discover optimized topological structures.
